Introduction
The shoulder is one of the most complex and versatile joints in the human body. It plays a crucial role in nearly every upper body movement, from lifting and throwing to reaching and rotating. However, due to its complexity, the shoulder is also prone to various issues, including pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. In this article, we’ll explore the anatomy of the shoulder, how it moves, its mobility, and how to maintain its function for optimal health.
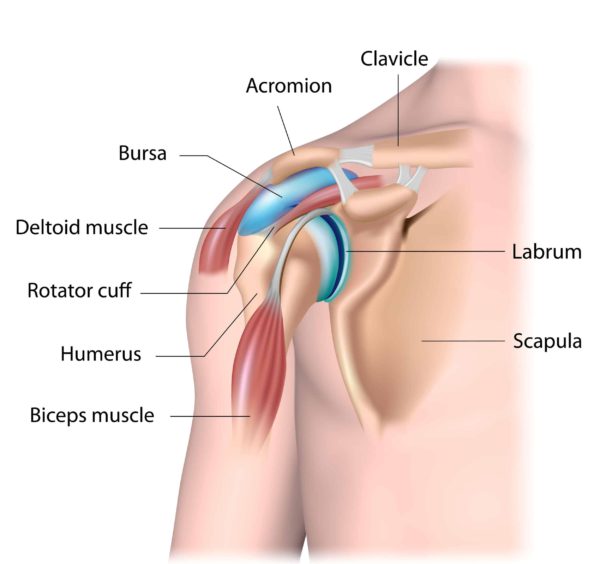
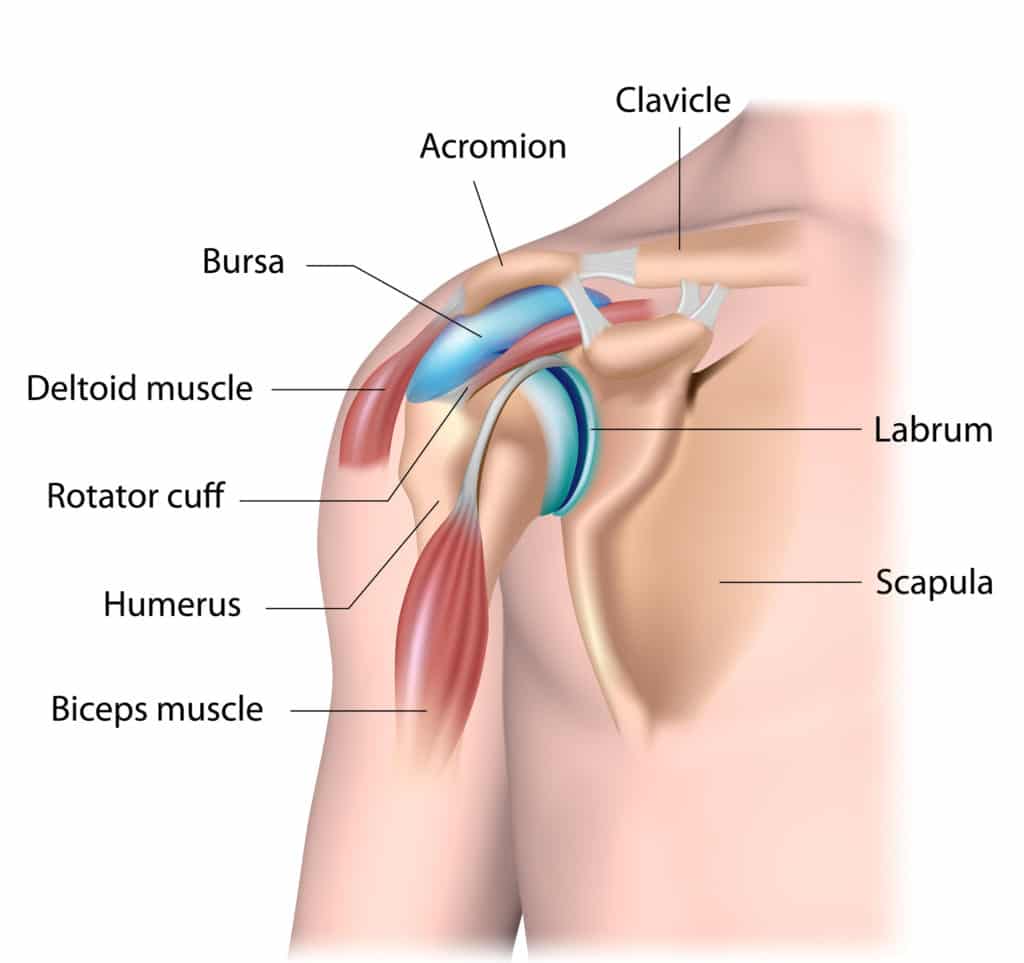
Anatomy of the Shoulder
It is a ball-and-socket joint that consists of two main bones:
- Humerus: The upper arm bone, which fits into the socket of the scapula
- Scapula: The shoulder blade, which provides a base for the socket.
- Clavicle: The collarbone, which connects the shoulder to the chest.
These bones are supported by muscles, tendons, and ligaments that work together to enable a wide range of movements.
Movement
The joint is unique in its ability to move in multiple directions. The main movements include:
- Flexion: Raising the arm in front of the body.
- Extension: Moving the arm backward.
- Abduction: Lifting the arm out to the side.
- Adduction: Bringing the arm back toward the body.
- Internal Rotation: Rotating the arm inward toward the body.
- External Rotation: Rotating the arm outward, away from the body.
These movements are essential for daily activities like reaching, lifting, and even simple tasks like combing your hair.
Mobility
Mobility refers to the range of motion (ROM) in the joint. Good mobility is essential for maintaining function and preventing injuries. Poor mobility can lead to compensatory movements, increasing the risk of injury in other parts of the body, such as the neck or lower back.
Factors Affecting Shoulder Mobility:
- Muscle Tightness: Tight muscles can restrict movement.
- Joint Stiffness: Inactivity or previous injuries can lead to joint stiffness.
- Posture: Poor posture, such as rounded shoulders, can limit shoulder mobility.
- Overuse: Repetitive motions, especially in sports, can cause wear and tear, affecting mobility.
Try this Shoulder mobility test at home
Maintaining Shoulder Function
To keep your shoulders healthy and functional, it’s important to maintain a balance of strength, flexibility, and stability. Here are some tips:
- Strengthen the Rotator Cuff: The rotator cuff muscles are critical for shoulder stability. Exercises like external rotations and shoulder presses can help strengthen these muscles.
- Improve Flexibility: Stretching exercises targeting the chest, shoulders, and upper back can enhance flexibility. Yoga poses like the downward dog and child’s pose are excellent for shoulder mobility.
- Practice Good Posture: Maintaining proper posture reduces strain on the joints. Regularly check your posture, especially if you work at a desk.
- Incorporate Mobility Exercises: Dynamic stretches, such as arm circles.
- Avoid Overuse: Be mindful of repetitive motions, especially if you’re involved in sports. Rest and recovery are key to preventing overuse injuries.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you experience persistent shoulder pain, stiffness, or a decrease in mobility, it’s important to seek professional help. A physiotherapist can assess, identify any underlying issues, and develop a personalized treatment plan. Early intervention can prevent further damage and restore full function.
Conclusion
Understanding your shoulders is crucial for maintaining overall shoulder health. Whether you’re an athlete or someone who wants to stay active, keeping them in top condition will help you perform daily activities with ease and reduce the risk of injury. If you’re experiencing any issues with your shoulder, consider booking an appointment. We’re here to help you get back to your best.
Bookings with a Physio
Triumph Physio in Newmarket or Mount Wellington, Auckland. We have qualified Physiotherapist registered under ACC to help you. For more info call us on 09 526 1448 or book online below